ROOTS & FRUITS OF AI – INFOGRAPHIC
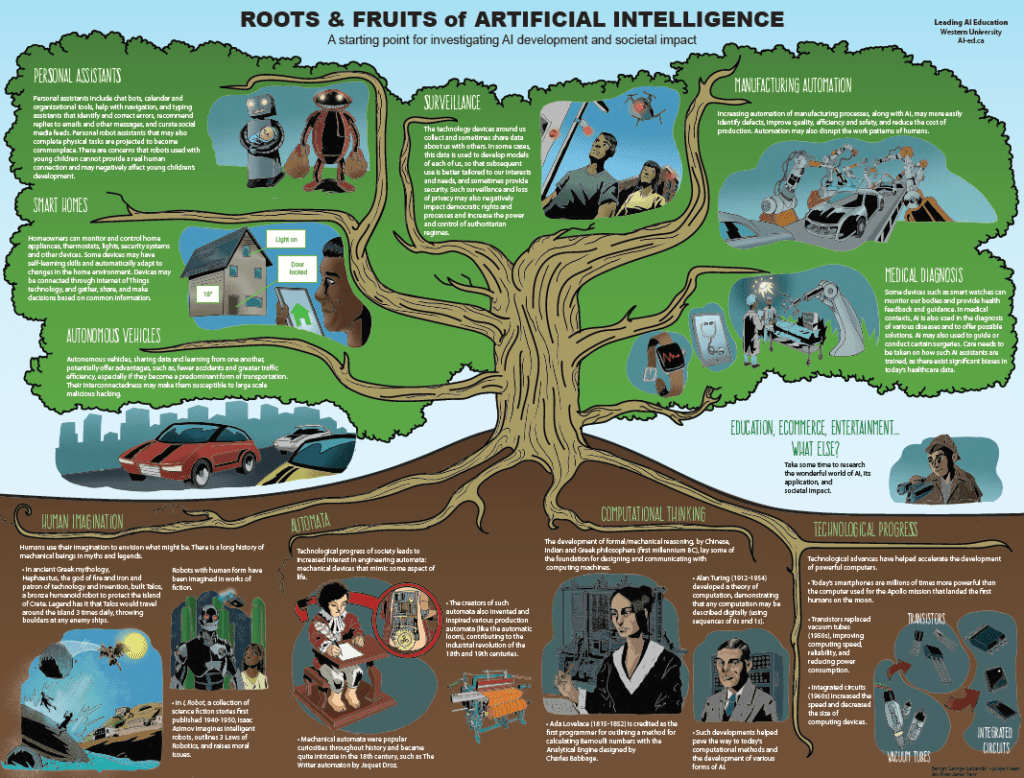
The Roots & Fruits of AI infographic provides an overview of the origins of AI (roots) and its use and implications for society (fruits).
- Where does AI come from?
- What is its impact?
- How does it fit in the curriculum?
Get the infographic PDF. Get the PDF for 6 activity prompts.
1. ROOTS OF AI
Where did the idea of creating AI come from, and what made its development possible?
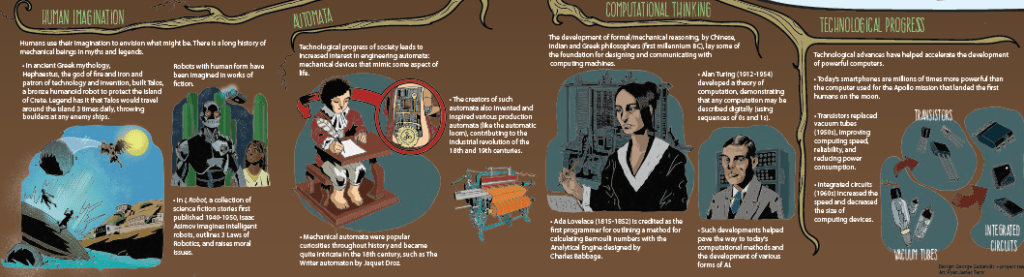
Below is a list if 4 elements that played important roles in the development of AI:
- Human imagination
- The development of mechanical automata
- The development of formal mechanical reasoning (computational thinking)
- Technological progress
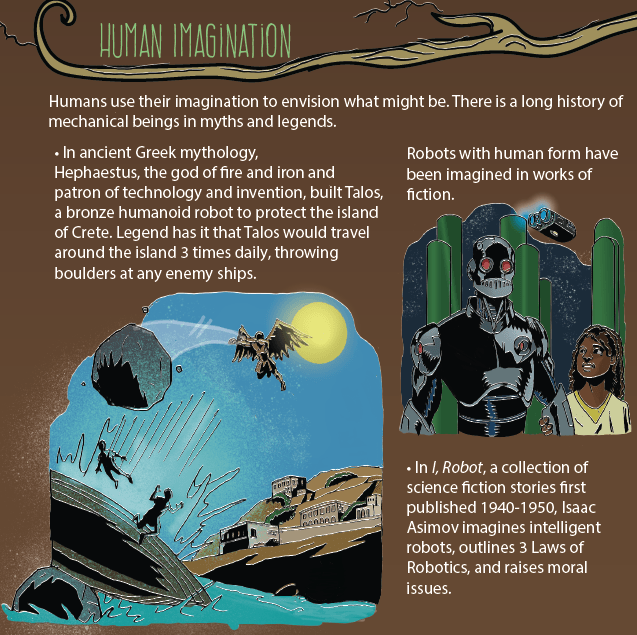
2. HUMAN IMAGINATION
Humans use their imagination to envision what might be. There is a long history of mechanical beings in myths and legends. Robots with human form have been imagined in works of fiction.
2.A. MECHANICAL “BEINGS”
What mechanical beings have you comes across in stories or movies?
What were they designed to do?
What was their role in their story or movie?
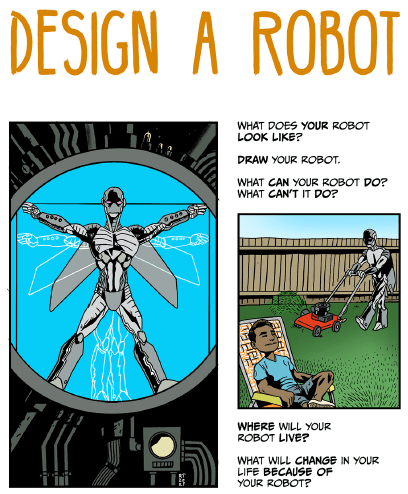
2.B. DESIGN A ROBOT
What does your robot look like? Draw your robot.
What can your robot do? What can’t it do?
Where will your robot live?
What will change in your life because of your robot?
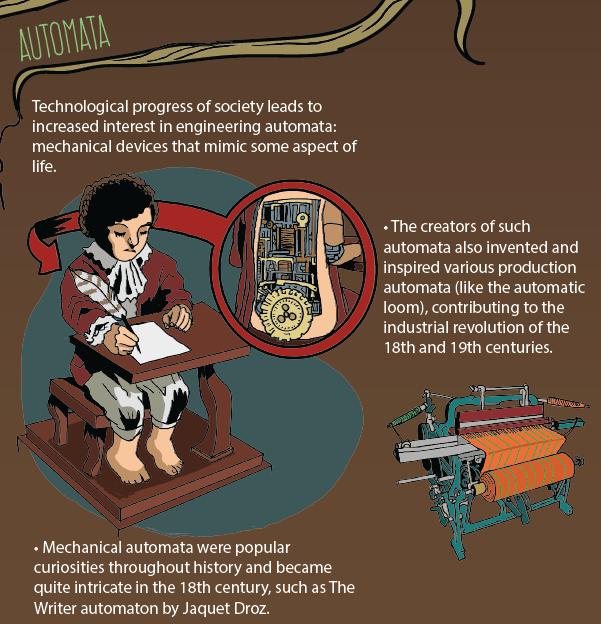
3. AUTOMATA
Technological progress increased an interest in engineering automata: mechanical devices that mimic some aspect of life.
3.A. DEVICES THAT MIMIC DAILY LIFE
What are some mechanical or electronic devices in your home or in your neighbourhood that mimic some aspect of daily life?
Note: a washing machine (washing clothes) and a traffic light (directing traffic) are two examples.
3.B. PIERRE JAQUET-DROZ AUTOMATA
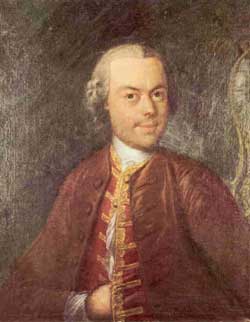
Pierre Jaquet-Droz (1721–1790), his son Henri-Louis (1752-1791), and Jean-Frédéric Leschot (1746-1824), build automata made of thousands of mechanical pieces.
“Some consider these devices to be the oldest examples of the computer. The Writer, a mechanical boy who writes with a quill pen upon paper with real ink, has an input device to set tabs, defining individual letters written by the boy, that form a programmable memory. It has 40 cams that represent the read-only program. The work of Pierre Jaquet-Droz predates that of Charles Babbage by decades.” (Wikipedia)
View the video below.
- What surprised you?
- What questions do you have?
- Conduct an Internet search to find other people who designed and developed such automata.
3.C. DESIGN AN ABSTRACT AUTOMATON
Automata do not have to be physical. They can be abstract.
Like a diagram of how a mechanism works.
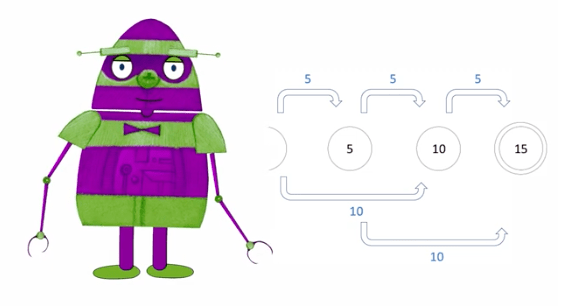
Example: Let’s build abstract automata of how turnstiles and vending machines work.
- Abstract automata help describe, analyze, and understand discrete systems, like computers.
- The inputs and outputs of discrete systems are either ON or OFF (1 or 0).
- Abstract automata are used in the development of computational theory.
Extend: Work with a partner to create the abstract automaton for a vending machine where snacks cost 25 cents.
3.D. CELLULAR AUTOMATA
Run the Python code for producing Cellular Automata.
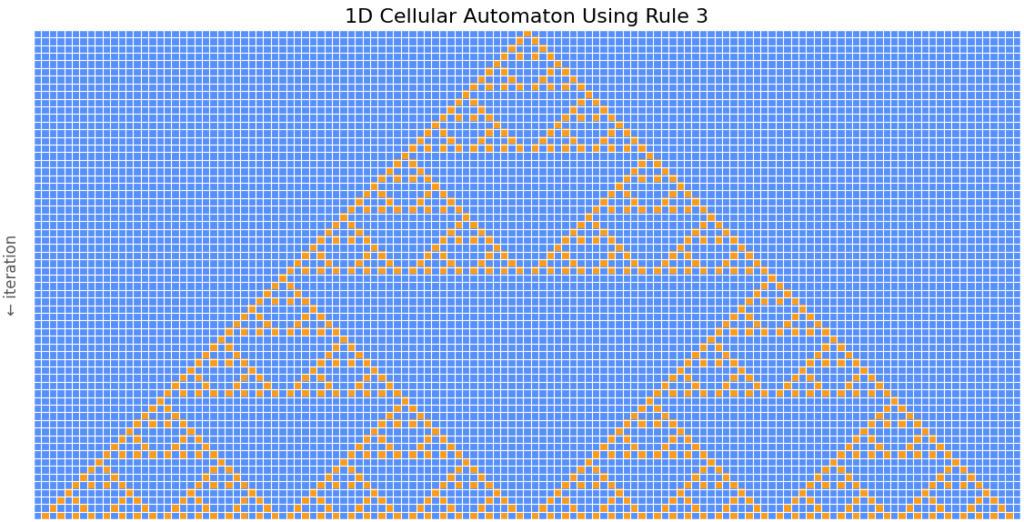
Edit the code to produce new variations.
4. COMPUTATIONAL THINKING
How did computers become “thinking” machines?
4.A. THINKING MACHINES?
Do machines think?
- In what way is machine thinking different than human thinking?
- In what way is it similar?
Are machines better at thinking than humans?
- In what way are they or are they not?
4.B. HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENTS
With your partner, select and research a historical person who contributed to the development of machines that “think”. For example, Ada Lovelace, Charles Babbage, and Alan Turing.
- Create in infographic about their life and contributions.
- Or, author the dialogue for an interview skit with a person who contributed to the development of machines that “think”.
4.C. RECENT AI DEVELOPMENTS
With your partner, select and research a recent AI development.
Create in infographic about this AI development.
How might this development change our lives?
5. TECHNOLOGICAL PROGRESS
Technological advances have helped accelerate the development of powerful computers and the development of AI.
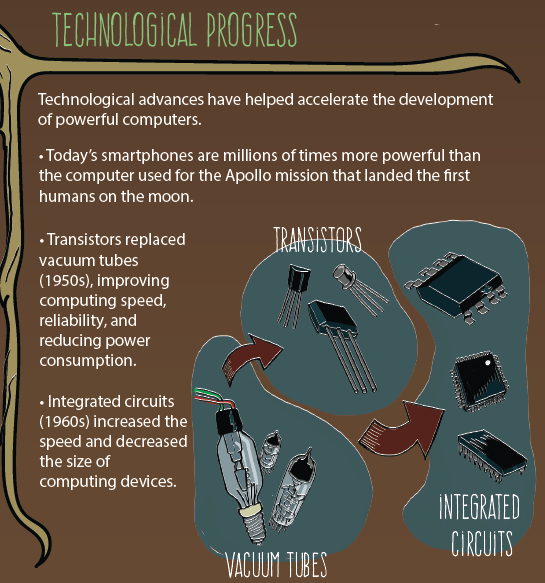
5.A. TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCES
What technological advances have you seen in your lifetime?
- For cellphones?
- For automobiles?
- For appliances?
- What else?
5.B. HISTORY OF COMPUTER DEVELOPMENT
Research the history of computer development.
- How are today’s computers different from the earliest ones?
- How has the use of computers changed over time?
- How has AI developed over time?
- How has the use of AI changed over time?

6. FRUITS OF AI
What are some of the applications and implications of AI in society?
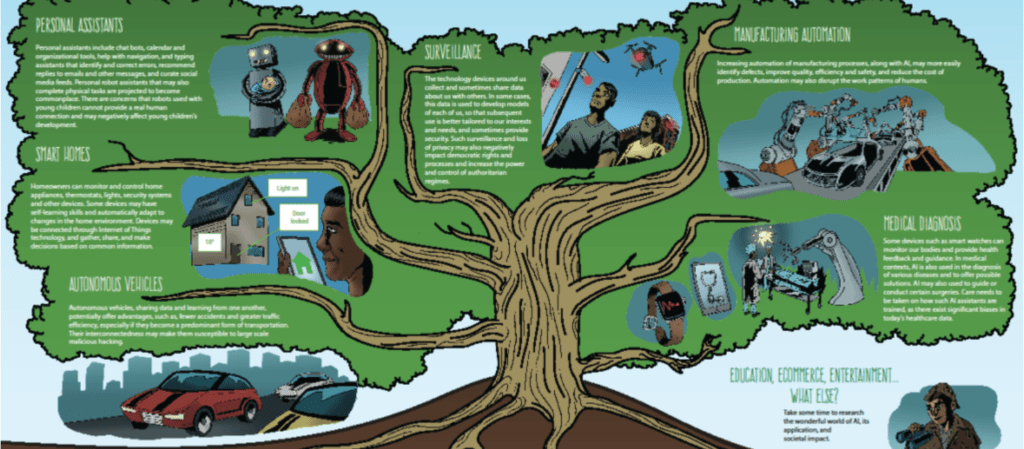
6.A. SOCIETAL IMPACT
Which “fruits” of AI illustrated below have the greatest impact on society? Why?
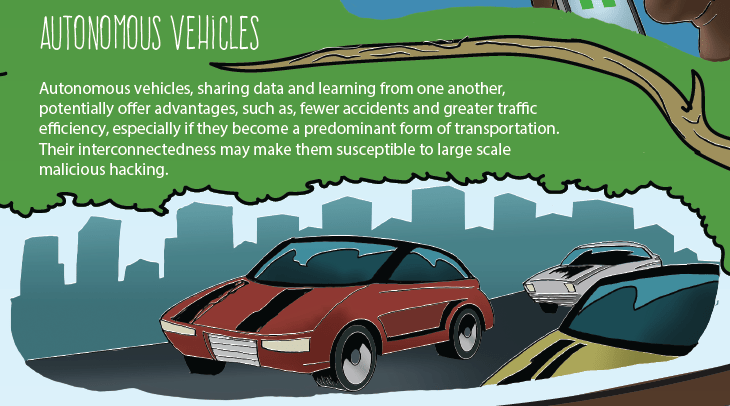
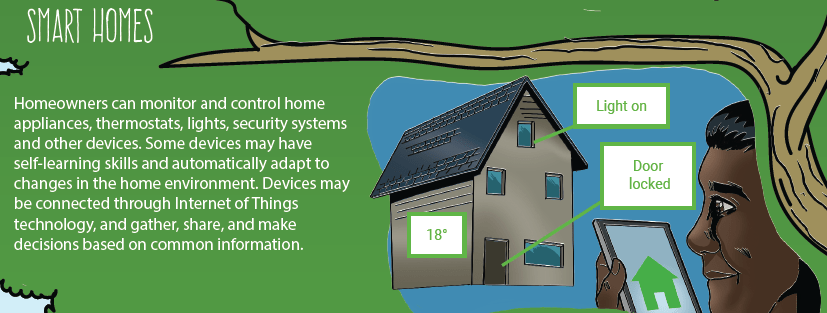


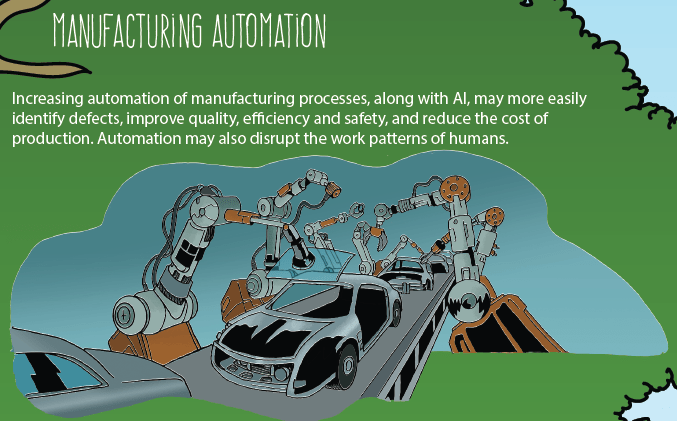
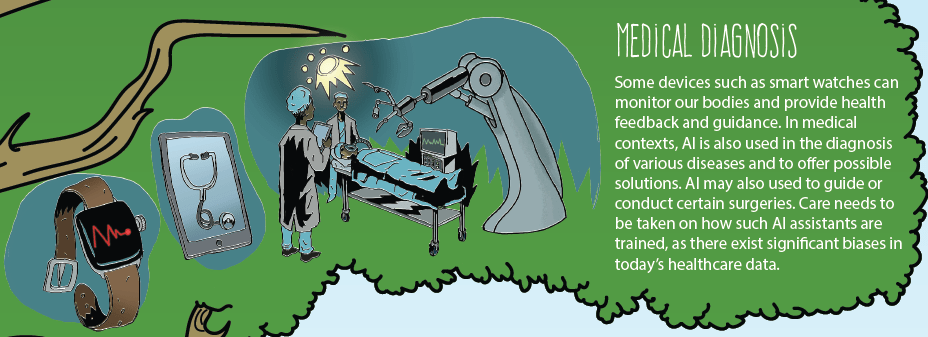
6.B. DEVELOP AN INFOGRAPHIC
Research and develop an infographic for a “fruit” of AI that interests you.
- What is its function?
- What is its effect on society?
- How might it evolve in the next 10-20 years?
- What will be the consequences?